 15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations
15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With IllustrationsTypes of thrombosis How thrombosis begins The arteries carry blood from your heart to your organs; the veins send it back to your heart. Sometimes the smooth flow of blood through these "pipes" slows down or crashes. Or, there's damage inside a blood vessel. That's when the blood cells can join and form a clot. Doctors call this thrombosis. Serious problems may occur, depending on where the clot is. Deep Veinte Thrombosis (DVT)A "deep vein" is further within your body, far from your skin. DVT occurs mainly in the leg or pelvis (minor-extremity thrombosis), but you can get it on your arm or shoulder (high-extremity thrombosis), too. Small clots sometimes dissolve alone. Large clots that do not move or disappear can block the flow of blood in the vein. They're dangerous if they break up because they can travel to their lungs. Pulmonary Embolism (PE)This is a blood clot that formed elsewhere and has traveled through its bloodstream to its lungs. More often, it's from a vein in the leg or pelvis. You can block the flow of blood in your lungs, so they don't work as well as they should. It can also damage other organs because their lungs cannot supply enough oxygen. If the clot is very big or you have more than one, PE can be fatal. Femoral 20 thrombosis This is a clot in the long vein of your thigh. It usually doesn't cause symptoms, but sometimes it might have swelling, redness, and leg pain. Femoral vein clots may occur for many reasons: after surgery, when you are at rest, or if you sit for a long time, take birth control pills or have had DVT before. Paget-Schroetter Syndrome (PSS)It is a rare type of DVT that usually happens to a healthy young person who plays sports that use the upper arms a lot, such as swimming and baseball. The vein can be expressed by the muscles around it. This pressure, along with repeated movements, can cause a clot on the shoulder. Symptoms such as swelling, chest pain, and a blue skin color may suddenly appear. The PSS can be serious if it is not treated immediately. Myocardial infarction (heart attack)The arteries of your heart may be obstructed by a sticky fat called a plaque. A clot that forms on the plate could cut blood flow to your heart. If not treated quickly, part of the heart muscle may die. A heart attack usually causes a chest pain. Women may have other symptoms, such as back pain or fatigue. Superior Vena Cava thrombosis This large vein in the chest returns blood from your body superior to your heart. You usually get this type of clot because you have a tube called a central line (used to carry the medicine in your body) or a catheter in your vein. Your doctor may remove the tube to treat the clot or leave it inside. Either way, you'll probably need medications to thin your blood to prevent more clots. 20 Jugular thrombosis The two sets of jugular veins on the neck bring blood from your head and neck back to your heart. Dresses tend to form in these veins when you have a central line in them. Cancer, surgery, or the use of intravenous drugs can also cause jugular venous thrombosis. These clots could break down, travel to your lungs and become PE. Trombotic Stroke When a clot blocks blood flow in one of the arteries of the brain, that part of the brain begins to die. The warning signs of a stroke include weakness in the face and arms and problems of speaking. If you think you're having a stroke, you must act fast. It can cause lasting problems with talking or using a side of your body. The sooner they treat you, the better the chance your brain will recover. Brain Venous Sinus Thrombosis This is a rare type of hit. A clot in this part of your brain prevents blood from draining and returning to your heart. Backup blood can leak into the brain tissue and cause a stroke. This occurs mainly in young adults, children and babies. A blow is deadly. Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis It doesn't happen often, but a blood clot can form in a vein that crosses the space behind your eye shots. The most common cause is an infection that spreads from the nose, face or teeth. Other things, such as a head injury, can also cause it. The main symptoms are eye problems. Your eyes may hurt, look irritated or swollen, or lump, or you may find it difficult to control your movements. Twenty Retina Occlusion It is one of the most common reasons that older people lose sight of. A clot that blocks the flow of blood in the central vein in the retina (the tissue that covers the back of the eye), or the smaller side veins, prevents the blood from draining from the eye. The blood is filtered and can lead to serious vision problems, such as glaucoma or a retinal that is detached. May-Thurner Syndrome Your right iliac artery carries blood to your right leg. Your left-handed vein brings blood from your left leg back to your heart. These two blood vessels cross into your pelvis. Normally, that's not a problem. But in someone with May-Thurner syndrome, the artery tightens the vein against the spine, making it more likely a clot in the left leg. It is something to consider when a young woman has sudden inflammation in her lower body. Portal de Trombosis Veinte The portal vein carries blood from its digestive tract and spleen to its liver. People with cirrhosis or who are prone to clots can get one in it. A small clot usually does not cause symptoms, and your doctor may not treat it. But if the pressure builds up in the vein behind the clot, you could get a spleen, swollen belly and bleeding. Your doctor will treat these symptoms and may try to prevent the clot from growing. Budd-Chiari Syndrome A narrow blood clot or blocks the veins that carry blood from your liver to your heart. It's not the same as portal vein thrombosis, but it has some of the same symptoms, including a large spleen, swollen belly and bleeding. The main problem is with your liver. It doesn't work as well as it should. If it's very damaged, it might need a liver transplant. Renal 20 thrombosis A kidney disease called nephrotic syndrome can cause a clot in any of the veins that carry the blood away from their kidneys. You may not have symptoms with a slow growth clot. A clot that happens all of a sudden can give you back pain and low blood on your piss. When you have only one kidney or clots in both veins, your kidneys could stop working. Next Presentation Title1 Reviewed by IMAGES PROVIDED BY:1) BSIP Science / Source2) WebMD3) Evan Oto / Science Source4) Springer Medizin / Science Source5) MedicalRF / Science Source6) BSIP / Science Source7) MedicalRF / Science Source8) Medical Medical MedicalRF / Science Source9) "SCHWANBERG" VICTOR / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images10) PDSN / Medical Images11) Springer Medizin / Science Source12) Michael Abbey / Science Source13 / Science Source14) Nucleus Medical Media / Medical Images15) iStock / Getty Images16) 3D4Medical / Medical Images SOURCES:IQWiG on PubMed: What are you? "American Society of Hematology: "For patients: Blood Clothes. " Journal of Vascular Surgery: "A complete review of Paget-Schroetter syndrome." Cardiovascular Diagnosis " Therapy: "Patt-Schroetter Syndrome: Veloous thrombosis treatment and results. "American Heart Association: "Heart Attack Symptoms in Women." UNM's Comprehensive Cancer Center: "Obstruction of the Veins to the Heart (Higher Vena Cava Syndrome). "American College of Cardiology: "Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis." Medscape: "Internal Jugular Vein Thrombosis", "Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis Treatment & Management", "Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO). Harvard Health Publishing: "Trombotic Stroke". UpToDate: "Patient Education: Symptoms and Diagnoses (Beyond the Foundations),""Corbral Veal Thrombosis: Etiology, Clinical Characteristics and Diagnosis", "May-Thurner Syndrome", "Patto portal vein thrombosis in adults: clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management. "Stroke: "Diagnosis and Thrombosis Management Brain Venous. "Johns Hopkins Medicine: "Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST). "Merc Manual, Consumer Version: "Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis", "Portal Vein Thrombosis", "Budd-Chiari Syndrome", "Renal Vein Thrombosis". Cleveland Clinic: "Oclusion of the Twenty Retinal", "May-Thurner Syndrome".Leicester University, Virtual Autopsy: "Case 5: The Portfolio Circulation". Vascular Medicine: "Trombosis venous portal: When to treat and how?"National Organization for Rare Disorders: "Chiari Buda Syndrome."Sumorok, N. "Trombosis of Twenty Real," Nephrology Grand Rounds, NYU Langone Health, October 18, 2011. This tool does not provide medical advice. This work does not prohibit medical help. It is intended for general information purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be based on making decisions about your health. Never ignore the professional medical advice in the search for treatment due to something you have read on the WebMD site. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor immediately or call 911. WebMD Slideshows See our presentations to learn more about your health. Top PicksHealth SolutionsMore WebMD Policies About WebMD Network Our applications for advertisers © 2005 - 2021 WebMD LLC. All rights reserved. DMA does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Tromboflebitis What is thrombophlebitis? Trombophlebitis is inflammation of a vein caused by a blood clot. It usually happens in the legs. A blood clot is a solid formation of blood cells that unite. Blood clots may interfere with normal blood flow through your body, and are considered dangerous. Thrombophlebitis can occur in the veins near the surface of the skin or deeper, between the muscle layers. This condition usually occurs in the legs, but it is possible to develop thrombophlebitis in other parts of the body. Blood clots can cause swelling in the veins of the neck or arms, but this is rare. Trombflebitis affects the superficial veins and is a different condition than that of . The symptoms of thrombophlebitis include inflammation, redness and sensitivity on the affected vein. A blood clot causes thrombophlebitis. Inactivity, such as being in bed after trauma or surgery, is an important cause of blood clots. You can also develop a blood clot if you are still for too long, like during a plane or car trip. Staying, stretching and moving your feet periodically for long flights or drives can help reduce the risk of blood clots. The movement promotes circulation, which discourages blood cells from being united. You may also develop blood clots if you have injured your blood vessels. Trauma in the limb in question can cause damage to a vein. It may also support lesions in a blood vessel of intravenous needles or catheters (IV) during a medical procedure. This type of injury is a less common cause of blood clots. There are also some things that can cause blood to clot more easily. These include: The symptoms of thrombophlebitis depend in part on what type you have. You may experience the following symptoms near the affected area if you have any type of thrombophlebitis: Surface thrombophlebitis sometimes makes the affected vein grow visibly fat and red. In some cases, your doctor will not need to do any important tests to identify the problem. The appearance of the area and the description of your symptoms may be sufficient to diagnose this condition. If the appearance and description of the condition does not provide enough information for your doctor to perform a diagnosis, you can use an image technique to see if a clot is present. Options include a , a , and an MRI scan. In other cases, your doctor may choose to perform a . This involves injecting a dye into the vein that appears in the X-rays. Your doctor will take X-ray images to see if you have a clot. Your doctor may recommend that you take care of your state at home if you have superficial thrombophlebitis. You will be given instructions that may include: Your doctor may need to remove the vein if the one with superficial thrombophlebitis becomes permanently antiesthetic or painful, or if you have this condition in the same vein more than once. The procedure is known as the strip of veins. This type of procedure should not affect its circulation. The deepest veins in the leg can handle the increase in the amount of blood flow. Patients with superficial thrombophlebitis usually do not need blood thinner. However, if the clot is close to the union of one of its deep veins, blood degators can help reduce the risk that the surface clot will become DVT. If DVT is not treated, it can lead to a , or a blood clot in the lungs. A PE can be life-threatening. Stretch or walk around regularly if you sit on a desk for long periods or if you're making a long journey in a car or plane. Feeling too long can lead to thrombophlebitis. Your doctor will change your IV lines regularly if you are in the hospital. They can also give you medications to help prevent thrombophlebitis depending on your condition and other factors. Last medical review on June 12, 2017 related stories Read this next series of words

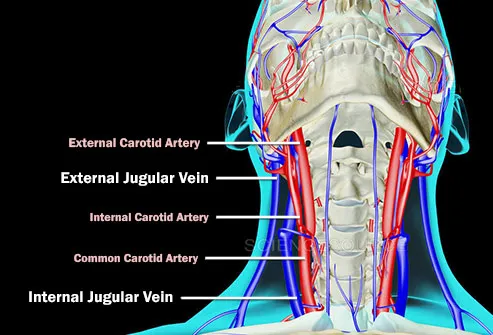
Cervical spine compression causes internal jugular vein stenosis – Caring Medical Florida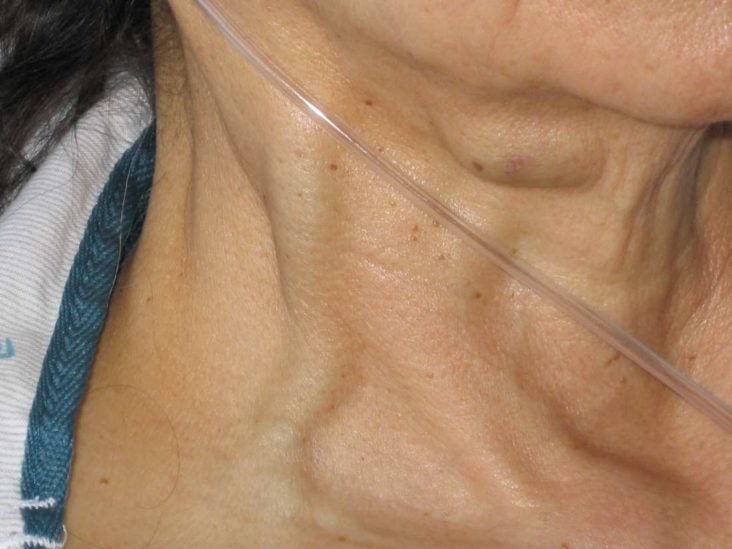
Jugular vein distention (JVD): Causes, risk factors, and diagnosis
Thrombosis of the External Jugular Vein: A Rare Complication of a Proximal Humerus Fracture Treated with Collar and Cuff Immobilisation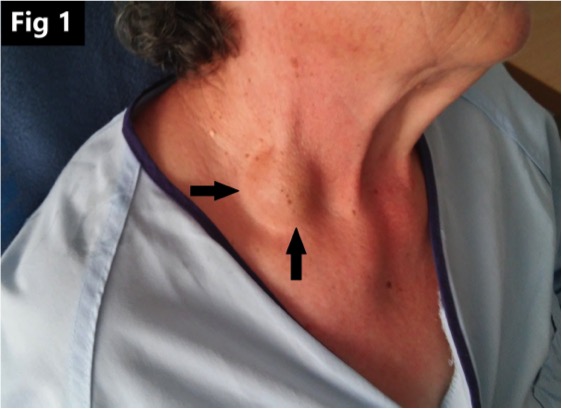
View of Idiopathic External Jugular Vein Thrombosis | European Journal of Case Reports in Internal Medicine
Photographs from fracture clinic demonstrating thrombosis of the... | Download Scientific Diagram
Heart Failure: A Dynamic Approach to Classification and Management | Clinician Reviews
Cervical spine compression causes internal jugular vein stenosis – Caring Medical Florida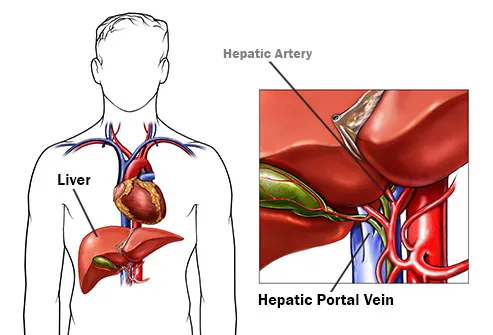
15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations
Thrombosis of the External Jugular Vein: A Rare Complication of a Proximal Humerus Fracture Treated with Collar and Cuff Immobilisation
Idiopathic External Jugular Vein Thrombosis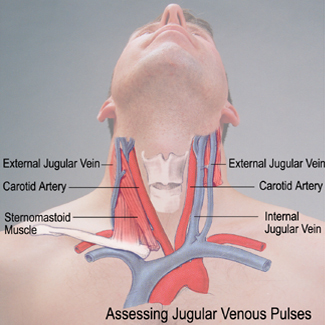
Closer Than Your Jugular Vein | HuffPost
Cerebral and Sinus Vein Thrombosis | Circulation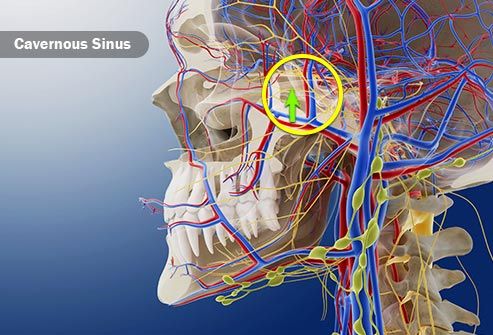
15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations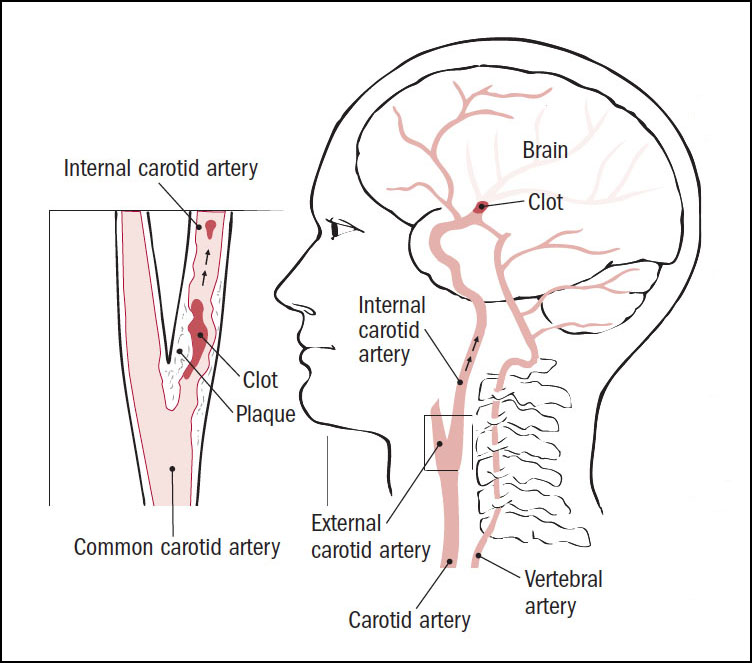
Carotid artery disease - Harvard Health/GettyImages-530309436-cf8e158016cf4dc0a81e12ecb221d1ee.jpg)
Internal Jugular Vein: Anatomy, Function, and Significance
Cerebral and Sinus Vein Thrombosis | Circulation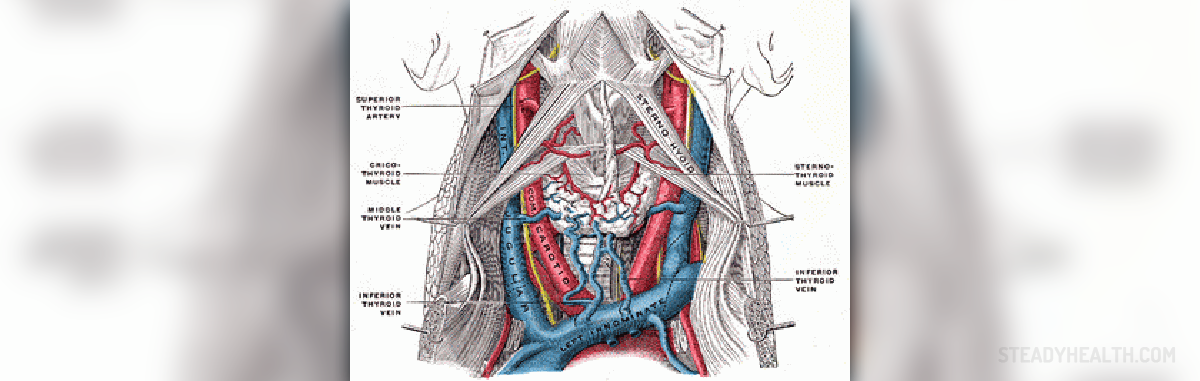
Symptoms of jugular vein thrombosis | Cardiovascular Disorders and Diseases articles | Body & Health Conditions center | SteadyHealth.com
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) - Cardiovascular Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional Edition:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overview-blood-clots-1745326_final-3990f6d12e19428e8734d92f068ce0de.png)
Blood Clots: Overview and More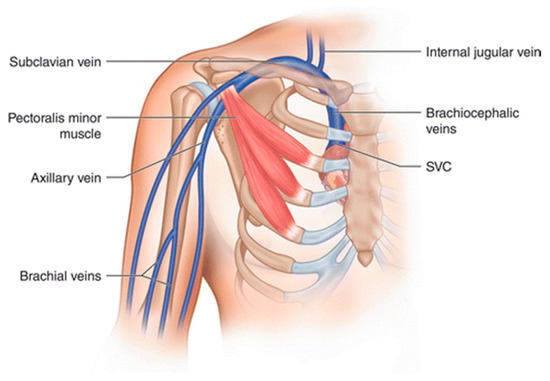
JCM | Free Full-Text | Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis | HTML
Photographs from fracture clinic demonstrating thrombosis of the... | Download Scientific Diagram
What is a partial thrombosis in jugular vein? - Quora
Pains in the Neck | Emergency Physicians Monthly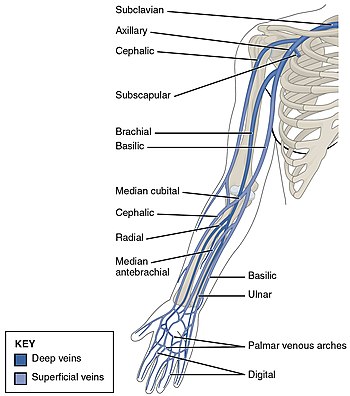
Deep vein thrombosis - Wikipedia
Understanding jugular venous outflow disturbance - Zhou - 2018 - CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics - Wiley Online Library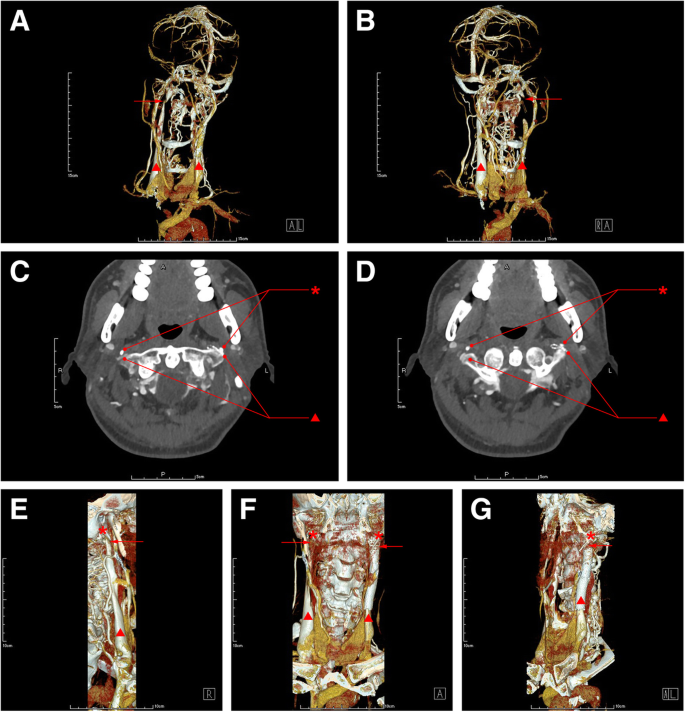
Internal jugular vein stenosis associated with elongated styloid process: five case reports and literature review | BMC Neurology | Full Text
External jugular vein thrombosis secondary to deep tissue neck massage - Journal of Vascular Surgery Cases and Innovative Techniques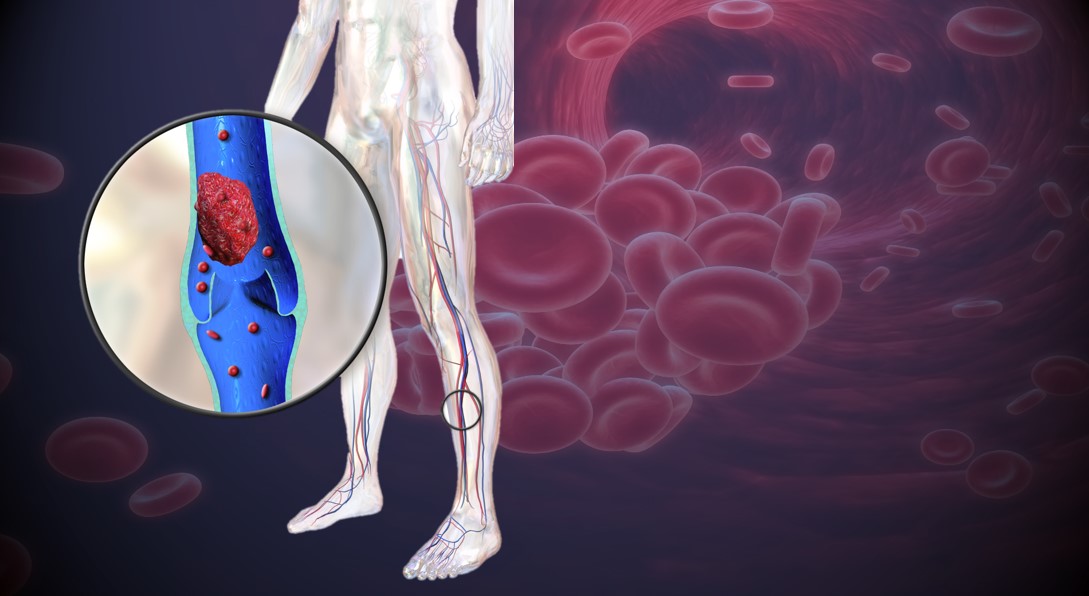
Symptoms of Blood Clot in Leg • MyHeart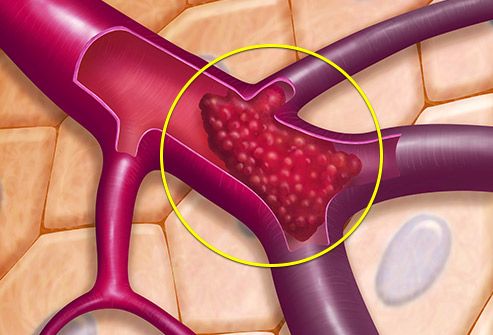
15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations
A Pain in the Neck That Almost Killed Me: Dan Jensen's Blood Clot Story | Blood Clots
What Is an Upper Extremity DVT?
Deep vein thrombosis - Wikipedia
Understanding jugular venous outflow disturbance - Zhou - 2018 - CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics - Wiley Online Library
Healthy Veins: Venous insufficiency, JVD, bulging veins in hands
11 Striking Facts About the Jugular | Mental Floss
My blood clot: no causes; just commentary – ordinary… mostly![Full text] Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis as primary presentation o | VHRM Full text] Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis as primary presentation o | VHRM](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_submission_image/s170000/170140/16_jul_2018_170140_fig190.jpg)
Full text] Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis as primary presentation o | VHRM
Pulmonary Embolism – DVT to PE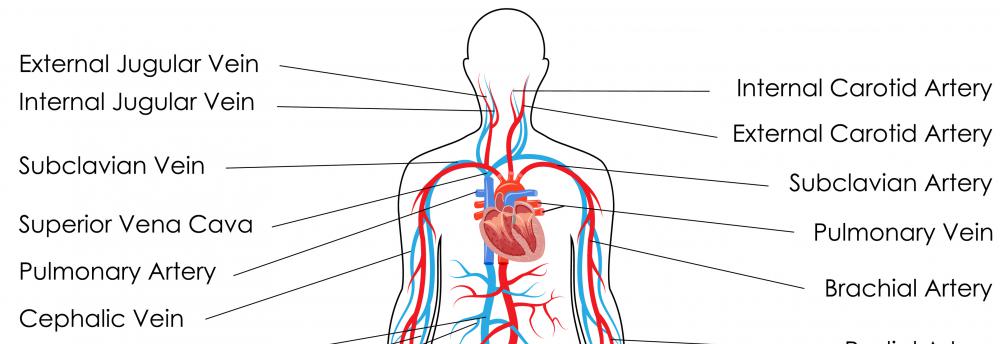
What is the Jugular Vein? (with pictures)
Central venous occlusion | Varicose veins | Vascular surgeon | Stroke | DVT | Leg gangrene | Cancer
 15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations
15 Types of Thrombosis Explained With Illustrations













/GettyImages-530309436-cf8e158016cf4dc0a81e12ecb221d1ee.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overview-blood-clots-1745326_final-3990f6d12e19428e8734d92f068ce0de.png)

















![Full text] Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis as primary presentation o | VHRM Full text] Spontaneous internal jugular vein thrombosis as primary presentation o | VHRM](https://www.dovepress.com/cr_data/article_submission_image/s170000/170140/16_jul_2018_170140_fig190.jpg)


Posting Komentar untuk "blood clot in jugular vein symptoms"